
Microsoft addresses 76 CVEs including two zero-days exploited in the wild, one of which was publicly disclosed
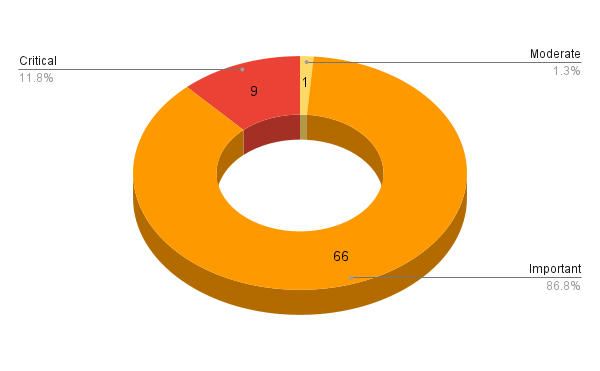
Microsoft patched 76 CVEs in its March 2023 Patch Tuesday Release, with nine rated as critical, 66 rated as important and one rated as moderate. This CVE count includes two CVEs (CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018) in the third party Trusted Platform Module (TPM2.0) Library.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- Azure
- Client Server Run-time Subsystem (CSRSS)
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Microsoft Bluetooth Driver
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft OneDrive
- Microsoft PostScript Printer Driver
- Microsoft Printer Drivers
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library
- Office for Android
- Remote Access Service Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
- Role: DNS Server
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Service Fabric
- Visual Studio
- Windows Accounts Control
- Windows Bluetooth Service
- Windows Central Resource Manager
- Windows Cryptographic Services
- Windows Defender
- Windows HTTP Protocol Stack
- Windows HTTP.sys
- Windows Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Partition Management Driver
- Windows Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
- Windows Remote Procedure Call
- Windows Remote Procedure Call Runtime
- Windows Resilient File System (ReFS)
- Windows Secure Channel
- Windows SmartScreen
- Windows TPM
- Windows Win32K
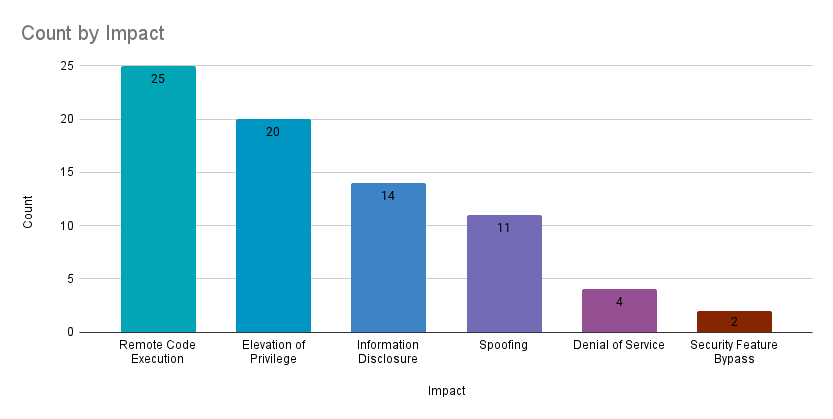
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 32.9% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 26.3%.
Critical CVE-2023-23397 | Microsoft Outlook Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-23397 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8 and was exploited in the wild. The vulnerability can be exploited by sending a malicious email to a vulnerable version of Outlook. When the email is processed by the server, a connection to an attacker-controlled device can be established in order to leak the Net-NTLMv2 hash of the email recipient. The attacker can use this hash to authenticate as the victim recipient in an NTLM relay attack. Microsoft notes that this exploitation can occur before the email is viewed in the Preview Pane, meaning no interaction from the victim recipient is needed for a successful attack.
The discovery of this vulnerability is credited to the Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine (CERT-UA) and Microsoft research teams.
On March 14, Microsoft published a blog post regarding the discovery of this vulnerability. In it, Microsoft says that they assess that a «Russia-based threat actor» exploited this vulnerability in «targeted attacks against a limited number of organizations in government, transportation, energy, and military sectors in Europe.» Additionally, Microsoft published a script that can be used to determine whether or not your organization has been targeted by this vulnerability.
Moderate CVE-2023-24880 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2023-24880 is a Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass vulnerability in Windows operating systems that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 5.4. The vulnerability has been publicly disclosed and was exploited in the wild. To be exploited, a malicious file needs to be opened by a user on an affected version of Windows. When the email is opened, the Mark of the Web (MoTW) functionality is bypassed, meaning that security features that rely on MoTW tagging are not triggered and could allow for malicious payloads within the file to be executed on the target.
Critical CVE-2023-23416 | Windows Cryptographic Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-23416 is a RCE vulnerability in Windows operating systems that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.4. The vulnerability exists in Windows Cryptographic Services, a suite of cryptographic tools in Windows operating systems. Exploitation is performed by importing a malicious certificate onto a vulnerable target, requiring the attacker to authenticate to the target or entice an authenticated user into importing the malicious certificate. CVE-2023-23416 was given a rating of «Exploitation More Likely» using the Microsoft Exploitability Index.
Critical CVE-2023-23415 | Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-23415 is a RCE vulnerability in Windows operating systems and was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8. The vulnerability lies in the way the operating system handles ICMP packets when an application running on the vulnerable Windows host is bound to a raw socket. Exploitation is performed by sending a malicious fragmented IP packet to a vulnerable target, leading to arbitrary code execution. CVE-2023-23415 was given a rating of «Exploitation More Likely» using the Microsoft Exploitability Index.
Critical CVE-2023-23392 | HTTP Protocol Stack Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-23392 is a RCE vulnerability in Microsoft operating systems that was given a CVSSv3 score of 9.8 and rated as «Exploitation More Likely.» The vulnerability exists in the HTTP. sys component of Windows operating systems. Exploitation can be performed by a remote, unauthenticated attacker sending a malicious packet to the target server. For a server to be vulnerable, it must have HTTP/3 enabled and use buffered I/O. The Microsoft advisory notes that HTTP/3 support is a new feature for Windows Server 2022 and must be enabled with a registry key.
Tenable Solutions
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced scan, in the plugins tab, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains March 2023.

